Contents
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Learn the importance of Bitcoin in this beginner’s guide. Discover how Bitcoin works, its uses, and how to get started on Gemini’s secure platform.
Summary
Bitcoin is the most well-known cryptocurrency, making waves in global finance. So, what exactly is it, and how can you take part? This beginner’s guide will walk you through the essentials.
Bitcoin 101
What is Bitcoin?
is a decentralized digital currency that was created by the pseudonymous developer .
It’s designed to work without the control of a central bank or government — it operates on a peer-to-peer network where users can make transactions directly with one another, bypassing intermediaries. This independence from traditional financial institutions allows Bitcoin to be both innovative and accessible.
Unlock the future of money on Gemini
Start your crypto journey in minutes on the trusted crypto-native finance platform
Bitcoin Is a “Virtual” Currency
As a form of virtual currency, , functioning through a transparent ledger known as Bitcoin blockchain. Each transaction is recorded on this distributed ledger, ensuring all the transactions remain secure and visible.
(like the US dollar), which central banks can print indefinitely, the amount of Bitcoin is limited to 21 million, a cap that increases Bitcoin’s potential as a store of value.
How Are Bitcoin Transactions Validated?
Every bitcoin transaction is broadcast by the node where the transaction originated to all the nodes in the Bitcoin network. These nodes make sure that the transaction is valid, meaning they scan the entire blockchain to confirm that the person sending money indeed has that money and is authorized to send it. If those two conditions are met the transaction is deemed valid.
Remember that Bitcoin is decentralized, which means that thousands of Bitcoin nodes in aggregate have to agree that a transaction is valid. Even if a few bad actors validated a transaction falsely, thousands of other nodes would not, and the transaction would not be confirmed. This makes the probability that a valid transaction is recorded extremely high and the probability that a false transaction is recorded extremely low — making Bitcoin incredibly safe and secure to use.
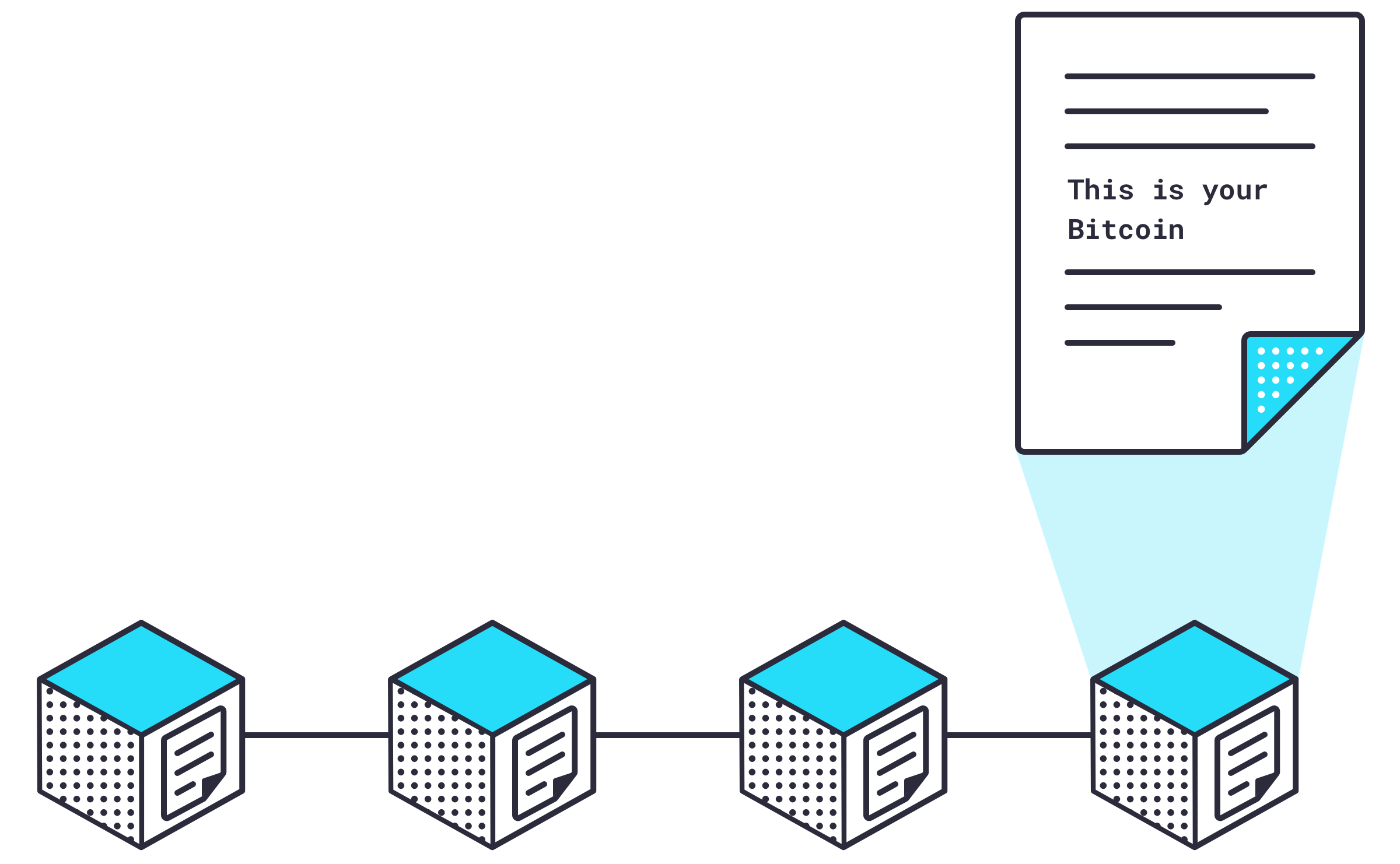
Every 10 minutes or so, all the latest valid transactions are organized into a block of data which is then sent out to the entire network to be secured in the blockchain.
A special subset of nodes called take unsecured blocks of data and do a couple of things to secure that block in the Bitcoin blockchain.
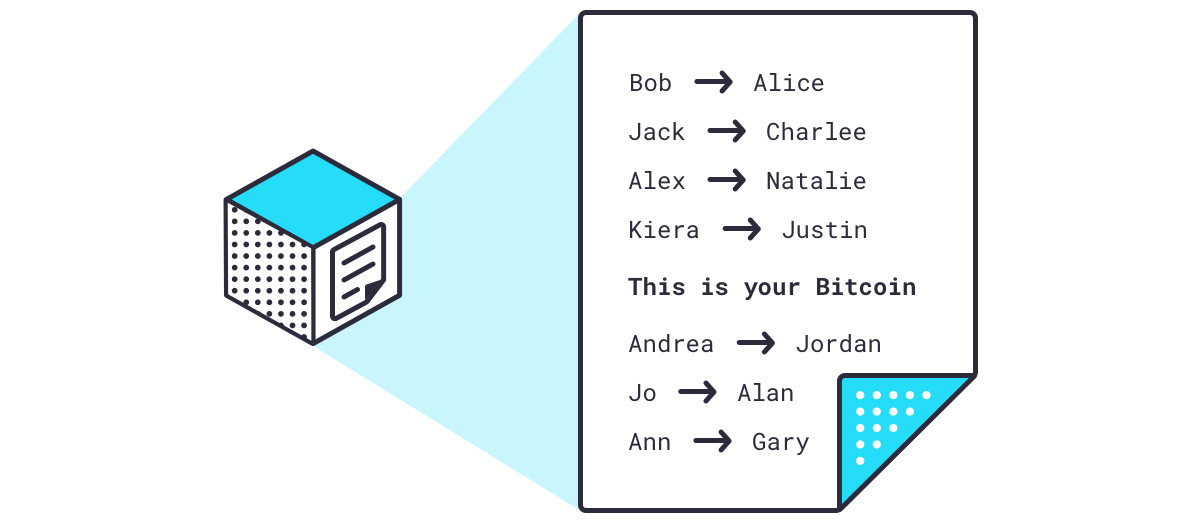
First, they take every transaction in the block and run it through an algorithm that takes each transaction and creates a unique identifying signature of 64 letters and numbers called a .
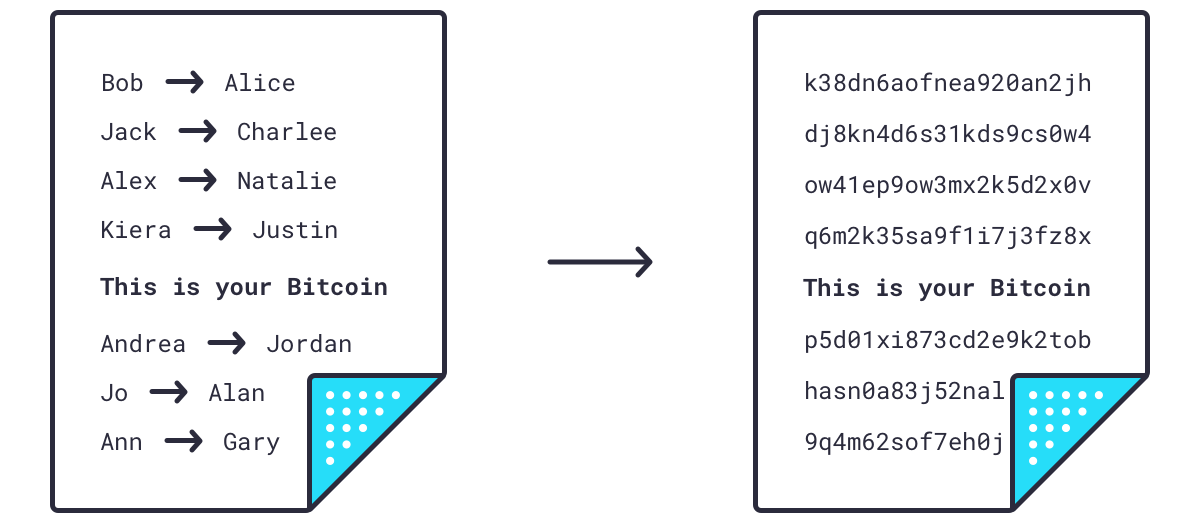
So now we have a block of transactions that have been compressed into hashes. They are then compressed further by pairing hashes together and creating a new hash for the pair. This is done until the entire block of transactions is represented by a single hash.
Then, the hash from the previous block is added to the block.
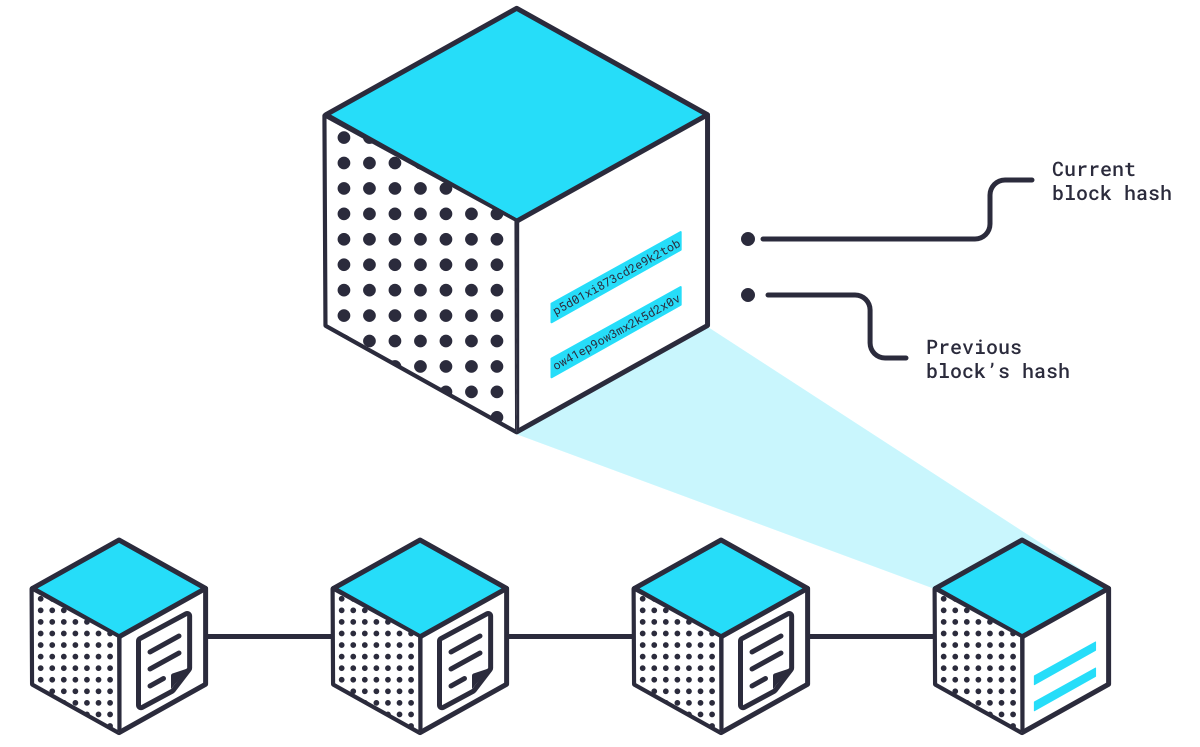
So now our block has the hash that represents all the current transactions in the block and the hash that represents all the transactions from the previous block. This is how the “chain” in “blockchain” is formed. If a single byte of data from any previous block were to change, it would invalidate all future blocks because every single hash going forward would change and break the blockchain.
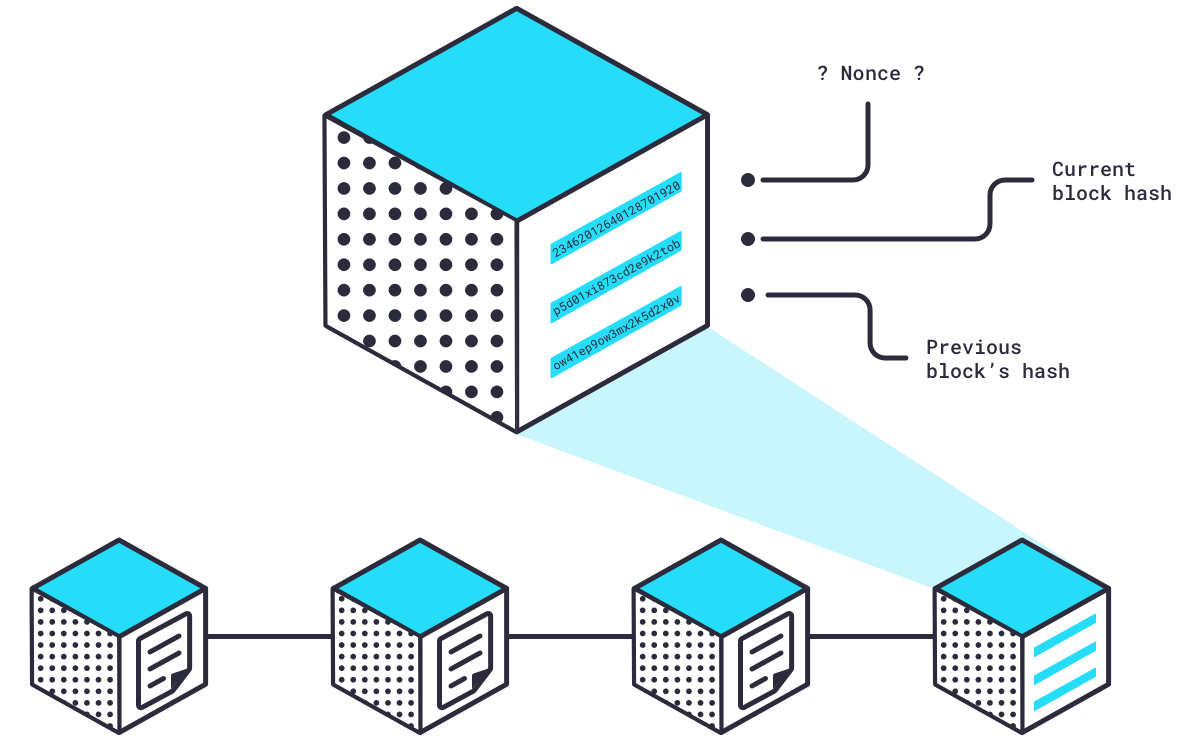
The final piece of the block is a random number called a , and this is where the miners really get to work.
The nonce and the two hashes in the block together need to create a hash that meets a certain set of criteria established by the software that powers the Bitcoin network. The only way to find a valid hash is by trying random nonce numbers until the hash criteria is met.
How Can I Use Bitcoin?
Bitcoin has a range of , from investments to everyday purchases.
Here’s a look at some of the most common ways to use Bitcoin:
Buying Bitcoin
To buy Bitcoin, you’ll need a digital wallet to store your Bitcoin (BTC). After setting up your wallet, the next step is choosing a reliable crypto exchange platform, such as , where you can .
These cryptocurrency exchanges guide you through the process, making it easy to start your crypto journey.
Spending Bitcoin
Bitcoin is increasingly accepted by both online and physical retailers worldwide. Major companies, including Paypal, Microsoft, and Shopify, now accept Bitcoin as payment, allowing you to buy goods and services and giving you the freedom to transact with this peer electronic cash system.
Legal and Secure Bitcoin Transactions
While Bitcoin is legal in most regions, it’s crucial to understand local regulations and use secure platforms. For extra safety, protect your Bitcoin wallet with measures like two-factor authentication and maintain a secure private key to access your funds.
What Is Blockchain?
, ensuring that every transaction is secure and trustworthy.
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that securely records each Bitcoin transaction. Each “block" in the chain contains information about multiple transactions, and once added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered. This immutability makes blockchain a reliable backbone for Bitcoin, ensuring each transaction is secure and tamper-resistant.
How Does Blockchain Secure Bitcoin Transactions?
Blockchain utilizes cryptography and complex algorithms to secure transactions. The consensus process ensures that each transaction is verified by nodes across the network, reinforcing Bitcoin’s security and transparency.
Blockchain Benefits for Bitcoin Users
The transparency and security that blockchain offers distinguish it from traditional financial systems. Bitcoin users benefit from a secure, accessible network that doesn't rely on intermediaries or banks, granting more freedom in managing their finances.
How Is the Blockchain Secured?
, develop algorithms, and spend a lot of time and energy in the form of electricity to find the nonce that meets this criteria. The first miner to find the nonce and create the hash that meets the criteria broadcasts the hash to the entire network.
While creating the block’s hash is very difficult, checking that it meets the criteria is very simple. Nodes verify that the block’s hash meets the criteria, then add that block to their copy of the blockchain.
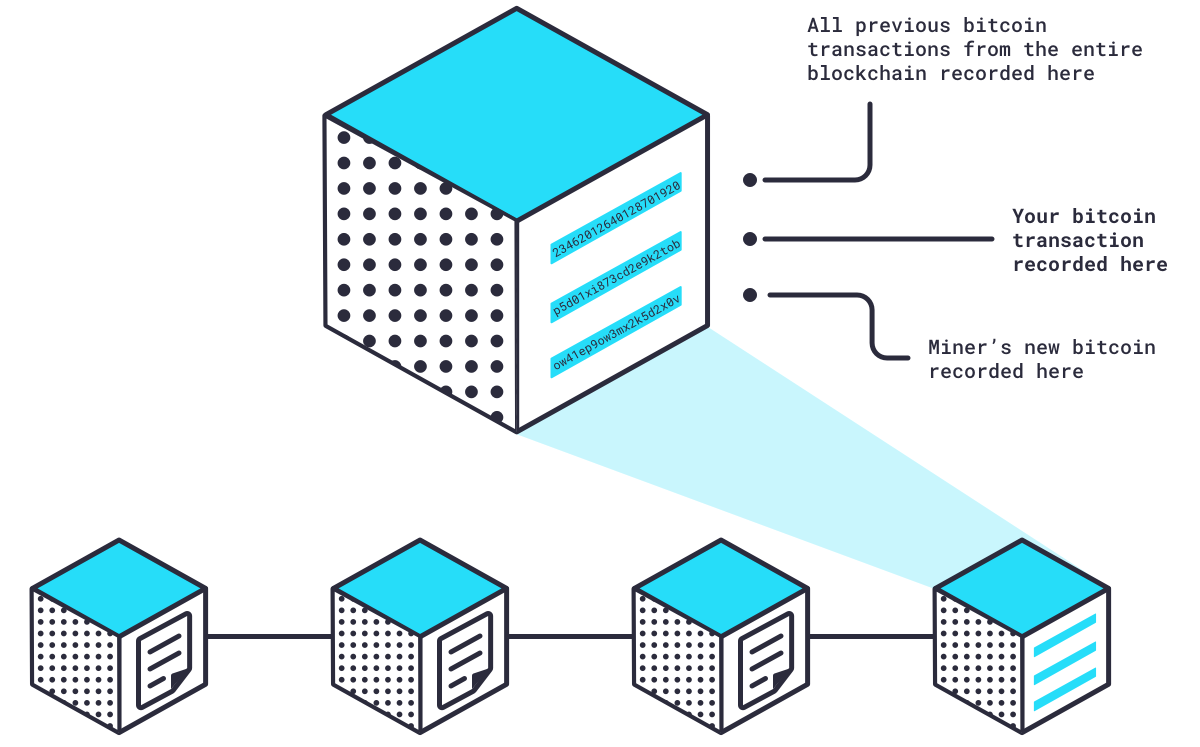
Remember, every Bitcoin full node keeps a copy of the entire blockchain, so the only way an invalid block can be added to the blockchain is if 51% of all nodes agree to its addition. While this is possible, it’s highly improbable, demonstrating another way that decentralization ensures a secure and accurate record of transactions on the blockchain. Valid blocks are added to copies of the blockchain all over the world and Bitcoin miners begin working on the next block.
In exchange for their effort, which is called , miners are rewarded with new bitcoin. This is the only way bitcoin is created.
So, another quick recap.
Transactions are turned into multiple hashes.
Those hashes are turned into a single hash.
That hash is combined with the hash from the previous block.
Those two hashes are combined with a nonce to create a unique hash for the new block.
The new block’s hash is verified by the network, added to all copies of the blockchain, and miners get paid in bitcoin.
The way that miners get their bitcoin is every mining team adds a transaction to the block in their node that states that they receive the pre-determined bitcoin for successfully mining that block. The team that actually does it, gets the bitcoin because their block is added to their copy of the blockchain, and subsequently all copies of the blockchain across the world. All other mining teams’ blocks are discarded.
What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining plays a vital role in maintaining the network and verifying transactions.
How Do Miners Verify Bitcoin Transactions?
using a process known as Proof of Work (PoW), where they solve complex mathematical problems. This adds new blocks of transactions to the blockchain, keeping the network secure and accurate.
The Mining Reward: Financial Incentives
To incentivize mining, miners receive new bitcoins as a reward. Over time, this reward decreases through , slowing the creation of new Bitcoin and reinforcing its scarcity.
However, the computing power required for mining is significant, and sustainability efforts are increasingly focused on making Bitcoin mining eco-friendly.
Is Bitcoin Mining Decentralized?
One of Bitcoin's defining features is its decentralized nature, which sets it apart from traditional financial systems.
Bitcoin Is Independent of Central Banks
In a decentralized network like Bitcoin, no central authority — such as a bank or government—controls the currency. Instead, thousands of maintain the network, ensuring its continued operation and security.
Advantages of a Decentralized System
Bitcoin’s decentralization means users have more freedom and security. Without central bank involvement, Bitcoin operates independently, offering financial freedom and resistance to censorship.
Challenges of Decentralization
While decentralization provides significant benefits, it can also present challenges, such as scalability and limited regulatory oversight. Nonetheless, Bitcoin’s structure is a powerful advantage for users seeking an alternative to centralized finance.
Investing in Bitcoin
Bitcoin has become increasingly popular as an investment asset, appreciated both for its potential high returns and as a store of value.
Due to its limited supply, Bitcoin is often seen as “digital gold.” Many investors view it as a way to protect their assets from inflation, offering a safe harbor in volatile markets.
Are There Risks to Investing in Bitcoin?
Like any investment, Bitcoin (BTC) comes with risks, including and regulatory uncertainties. However, with careful planning and diversification, investors can mitigate these risks and make Bitcoin a valuable part of their portfolio.
For beginners, it’s essential to approach Bitcoin with a long-term mindset and consider diversifying to minimize risk. Understanding the market and learning about the can provide deeper insights into its potential.
Bitcoin’s history has shown significant , but long-term trends indicate growing adoption and value. As more institutions and users adopt Bitcoin, its role in the financial landscape is likely to expand.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin's influence on global finance continues to grow, with its decentralized structure paving the way for a new era of digital currency.
Bitcoin is positioned to play a significant role in reshaping the world of finances, bringing freedom and innovation to users worldwide.
Ready to join the Bitcoin revolution? offers a trusted, secure platform to buy, store, and trade Bitcoin and other digital assets.
Discover why millions choose Gemini for their cryptocurrencies — today and take control of your financial future of Bitcoin.

Author
Is this article helpful?
