Contents
What Is Basic Attention Token in 5 Minutes
Basic Attention Token (BAT) is used on Brave Browser to provide private, fair, and mutually beneficial browsing for users, publishers, and advertisers alike.
Updated October 3, 2023 • 5 min read

Summary
Digital advertising is broken and Brave has developed a new, blockchain-based model to fix it. Brave actively blocks ads, malvertisements, and trackers so your browsing activity is safe, private, and fast. The Brave browser is built using Chromium, the open-source software that powers Google Chrome so all your favorite plug-ins and extensions work seamlessly. All you need to do to get started is to download the Brave web browser.
The Brave Internet Browser and BAT Crypto Asset
The free and open-source Brave web browser provides you with a faster, safer, more private, and more equitable internet browsing experience. Basic Attention Token (BAT) is its native utility token.
Digital advertising is broken and Brave has developed a new, blockchain-based model to fix it. Let’s take a minute to identify the stakeholders in today’s digital landscape and outline the problems they face, then we can dive into how the Brave browser and BAT are delivering a better internet.

Users
First and foremost there’s you, the user. You likely go online every day for a variety of reasons: to consume content like reading an article, watching a video, or listening to a podcast; to buy or sell products and services; or to communicate with friends, family, and colleagues.

Publishers (a.k.a. Content Creators)
The Brave browser concerns itself primarily with websites that deliver content, such as your favorite news site. That news site is called a publisher because it’s publishing content. It may be helpful to think of publishers simply as content creators.

Advertisers (a.k.a. Brands)
Publishers make money by selling space on their websites for brands to display advertisements. Brands buy space on publishers’ websites with the hope that you see their ads while you’re consuming content – and ideally choose to click on that ad to move further towards purchase.
Critical Issues in Internet Usage
With us so far? Good. Now let’s talk about some issues with this current model.
Problem 1: Speed
When you navigate to a publisher to consume content, a server collects and delivers that content to your computer. But, servers also need to collect and deliver ads from advertising exchanges, as well. This takes up precious time (ads use about five seconds of mobile load time on average) and costs you money (up to 50% of your mobile data is used for ads and trackers, costing as much as $23 a month) – not to mention decreasing your phone’s battery life by as much as 21%.
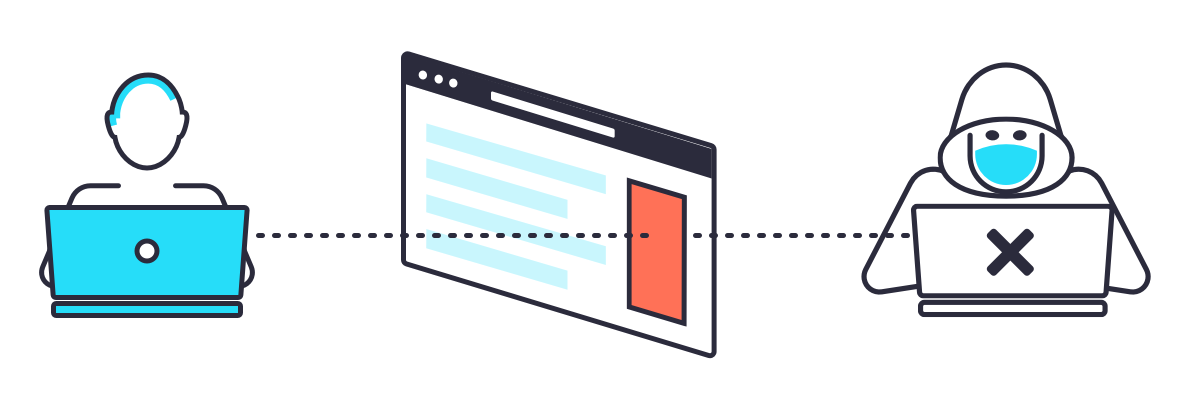

Problem 2: Safety
While you may not be aware of it, alongside the regular advertisements that are served to the websites you’re browsing come malicious advertisements. Malicious advertisements, also known as malvertisements, allow hackers to gain access to sensitive and important information stored on your computer like your name, address, date-of-birth, social security number and credit card number. And, you don’t even necessarily need to click on these malvertisements for them to gain access to your information!

Problem 3: Privacy
Publishers not only sell space on their platforms for advertisers to display their ads, they also track the content you consume on their website (usually by dropping a cookie). Combined with your computer’s IP address, publishers sell your unique profile back to advertising exchanges so they can, in turn, serve you more targeted ads across all the websites you browse. If you’ve given your personal information at any point to a publisher to buy or subscribe to content, those advertising exchanges now know your actual identity as well.
All these problems ultimately come down to one thing: cost. Cost of your time, cost of your privacy, and cost of your safety, which ultimately means cost of your hard-earned money.
There are a number of issues with this current model that are also harmful to publishers and advertisers. For example, advertising exchanges take huge percentages (more than 70%) of publishers’ advertising revenue for serving those ads to publishers’ websites. Also, publishers don’t make money when users have ad blockers and currently more than 600 million devices run ad blockers. And, advertisers don’t really know how effective their ads are unless a user directly clicks on the ad.

Advantages of Brave Browser
As a baseline, Brave actively blocks ads, malvertisements, and trackers so your browsing activity is safe, private, and fast. If that’s all you want or need, they deliver: for free. The Brave browser is built using Chromium, the open-source software that powers Google Chrome, so all your favorite plug-ins and extensions work seamlessly. All you need to do is download Brave and start browsing.
However, there are a number of aspects to the Brave ecosystem that can further benefit you, advertisers, and publishers – and this is the perfect time to talk about Basic Attention Token, or BAT, an Ethereum-based utility token tied to the Brave browser.

BAT Rewards
You can earn BAT tokens from advertisers by actively opting in and choosing to view ads.

When that ad is served alongside the content you’re consuming, the Attention Value for the ad, i.e., the amount of BAT you earn, will be calculated based on how much time that ad is visible in your active tab and the number of visible pixels of the ad in proportion to the number of pixels that make up the rest of the content on the page.

When you opt-in to earn BAT tokens by viewing advertisements, publishers also earn BAT because their content brought you to the website where those ads are served in the first place. Publishers are incentivized to create great content, so you can earn together. The more time you spend viewing their content and the ads that are served alongside it, the more BAT they earn. One other great feature of the Brave browser’s BAT rewards ecosystem is that you can tip with BAT tokens on an ad-hoc basis, or donate BAT on a recurring basis, to your favorite publishers to reward them directly for giving you great free content. Or, you can even use BAT to buy premium content or services from publishers directly.
And, finally, brands can now more clearly see how effective their ads are thanks to Brave’s ingenious Attention Value system.
Brave Browser Privacy
With Brave, your behavior across websites never leaves your browser. That means, no profile of your activity or your identity is shared with any third-party. Rather, Brave uses machine learning within the browser to determine what ads to serve to you from a pool of ads created by brands that partner with Brave. This profile always remains local to your browser so your activity stays private and you can delete this local profile at any time.
You may be asking yourself, “why do we need to bother with BAT when we can use dollars?” The answer is privacy. To earn or tip or donate fiat currency like dollars, you would need to reveal your identity and financial information to participate in the Brave ecosystem. With BAT, transactions are public on the Ethereum blockchain, but your identity remains private!
With BAT and the Brave web browser, you, content creators, and brands can all coexist online in a safe, private, and mutually beneficial ecosystem.
Note: Brave is actively building and evolving their browser and ecosystem. Some elements of the Brave browser and BAT token reward system may be in earlier stages of development than described above.
Cryptopedia does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Cryptopedia article are solely those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions of Gemini or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice. A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions. Please visit our Cryptopedia Site Policy to learn more.

Is this article helpful?