Contents
What is Uniswap? A Breakdown
The Uniswap (UNI) protocol is a paragon of the power of dApps, and a driving force behind the rapid growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
Updated October 3, 2023 • 4 min read
Summary
Uniswap is one of the largest decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges by transaction volume, and a leader within the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. The Uniswap platform is a blockchain protocol that uses automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools to facilitate peer-to-peer trading. Liquidity providers add tokens to Uniswap pools and are rewarded with a fee proportional to their share of the pool.
Within the world of traditional finance, stock exchanges provide a market in which equities, commodities, currencies, bonds, derivatives, and other financial instruments are traded, while forex markets provide a venue for the exchanging of national currencies. These exchanges provide a crucial source of market liquidity and are central to the stability of the global financial system. Cryptocurrency exchanges emulate this marketplace dynamic, offering a venue for trading digital assets in a format which closely resembles traditional online equity markets.
Although cryptocurrencies rely to some extent on decentralized blockchain technology, many of the world’s leading crypto exchanges remain inherently centralized. Despite the well-recognized benefits of centralization such as robust liquidity and fast settlement times, concerns over individual user autonomy are driving the development of decentralized exchanges (DEXs). These emerging alternatives are fully enabled by blockchain technology and use smart contracts to execute transactions between buyers and sellers in an automated, trustless fashion.
Nevertheless, decentralized exchanges have faced growing pains and are bound by the current limitations of blockchain technology. To date, issues of network scalability, segmented liquidity, and disjointed user experience have posed significant hurdles to widespread DEX adoption. To address these shortcomings, protocols like Uniswap are developing tools to improve the functionality of DEXs. As pioneers of liquidity pool mechanisms and the wider decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, Uniswap has grown into the largest DEX in the world.
Uniswap 101
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange protocol that operates on the Ethereum blockchain. The platform enables peer-to-peer (P2P) cryptocurrency trades that execute without order books or a centralized intermediary. The Uniswap platform achieves this with a liquidity pool model that uses automated smart contracts to enable prospective traders to access competing user-funded token reserves as the primary source of market liquidity. Anyone can swap tokens, contribute tokens to a pool and earn fees, or list a token on Uniswap. Since Uniswap is built on Ethereum, almost any ERC-20 token is exchangeable using Uniswap. Furthermore, there are no listing fees for a token to be available for trade on Uniswap — a noteworthy departure from most centralized crypto exchanges.
In conventional markets, order books compile an exchange’s open buy and sell orders for any asset. If there's a substantial gap between the prices buyers are willing to pay and those that sellers are willing to accept, the resulting lack of trading activity leads to decreased liquidity. This means that if you hold an asset affected as such, it will be more difficult to sell. Uniswap pools minimize this misalignment between buyer and seller market orders by creating a deep reservoir of assets to trade, which in turn helps to mitigate potential market liquidity issues. Additionally, Uniswap’s automated market maker technology algorithmically analyzes liquidity pools to offer the most appropriate prices for specific trades.
How Uniswap Works
The key innovation that makes the Uniswap protocol work is automated market maker (AMM) technology. An AMM is a smart contract that manages the Uniswap pools that provide the tokens which are used to effectuate a trade. When a trade is made, Uniswap’s AMM algorithm determines the token’s effective price based on the supply and demand dynamics between the involved tokens in these liquidity pools.
When users trade with a Uniswap liquidity pool, the platform currently charges a transaction fee of 0.3%. Any user who contributes to a Uniswap liquidity pool receives a fraction of these fees proportional to their staked share of the entire pool. For instance, if the fees collected in a particular market equate to $100 and you provided 50% of the pool's liquidity, you receive $50. Uniswap does not collect any of the transaction fees charged on its platform; instead, profits are distributed solely among Uniswap’s community of users.
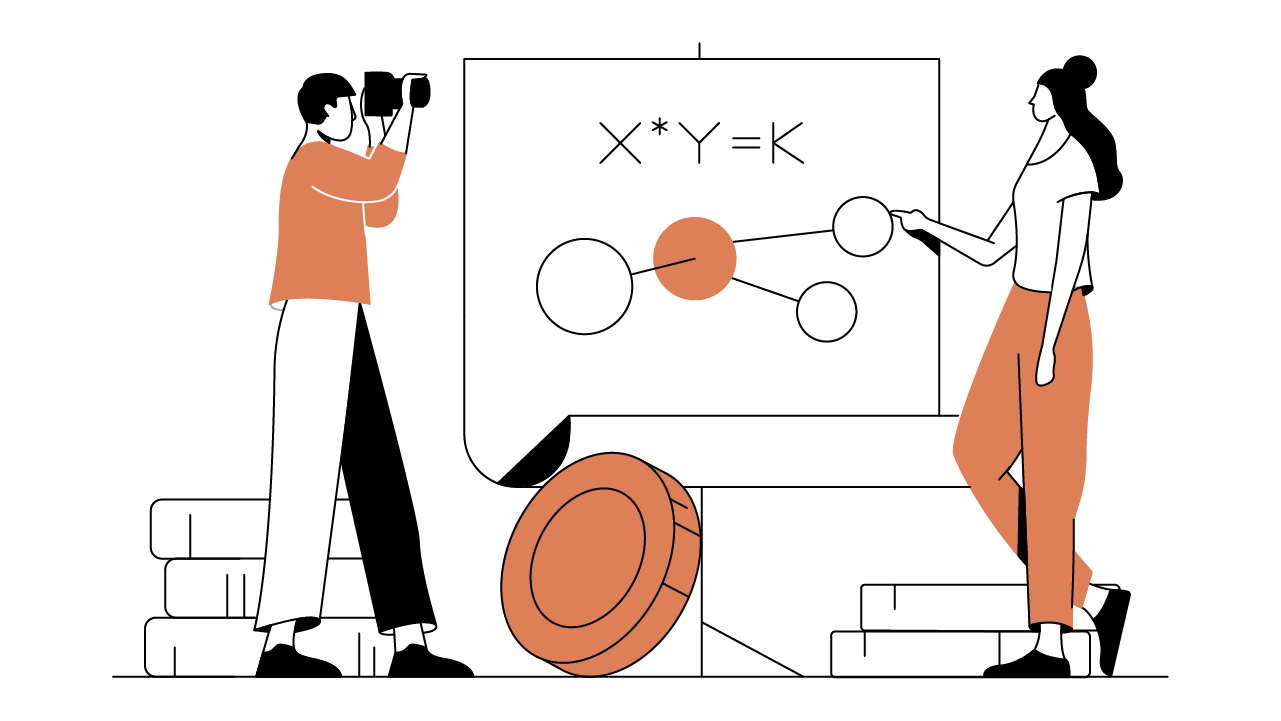
The Constant Product Formula
Each market pair of ERC-20 tokens held in a liquidity pool (e.g., ETH/DAI) is governed by an AMM built to accept one token for the other by maintaining what’s known as the "constant product" formula of x*y=k. In this formula, both x and y are variables that represent the total value of one token in the market pair. For example, x is the total value of ETH and y is the total value of DAI in a proposed ETH/DAI liquidity pool. Uniswap multiplies these two numbers together to determine k, which represents the market pair’s pool liquidity.
The core requirement which underpins trades on Uniswap is that pool liquidity remains constant, even as the values of x or y change. As a result, while every trade impacts the price of x and y, liquidity remains constant. For example, if a trader buys 1 ETH in exchange for 330 DAI, the ratio of ETH in the liquidity pool decreases, while the DAI ratio increases to accommodate one less ETH in the pool and 330 more DAI tokens. As a result, the price of ETH will increase, while the price of DAI drops. This formula ensures the maintenance that reflects fair market value while always maintaining liquidity.
Uniswap Governance: UNI Token
In September 2020, Uniswap introduced UNI, a native governance token that facilitates greater community involvement and oversight. UNI holders can vote on Uniswap project developments that determine the platform's evolutionary trajectory. UNI holders can also use the token to fund liquidity mining pools, grants, partnerships, and other growth-driven initiatives that expand Uniswap's usability and reach. As the Uniswap community grows, further diversifying UNI holdings, the founding team will play an increasingly diminished role in platform governance by design. This is evidence that the concepts of decentralization and alignment of incentives — both central to the DeFi revolution — are being put into practice by Uniswap.
Following a common token distribution trend in the DeFi ecosystem, Uniswap executed an airdrop of 400 UNI tokens to anyone who had used the platform — equating to a value of around $1,400 at the time of transfer — to approximately 250,000 Ethereum addresses. Although UNI serves as a governance token on the Uniswap platform, investors can also trade the token on exchanges and treat it as a speculative investment.
Uniswap Momentum
The Uniswap protocol is a major player among decentralized exchanges, and is one of the driving forces behind the accelerating growth of DeFi products and services. Uniswap’s recently issued UNI governance token builds upon the principle of community self-sufficiency by enabling stakeholder involvement in protocol decision making, and the platform itself serves as a successful model of what decentralized applications (dApps) are capable of.
Cryptopedia does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Cryptopedia article are solely those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions of Gemini or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice. A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions. Please visit our Cryptopedia Site Policy to learn more.

Is this article helpful?