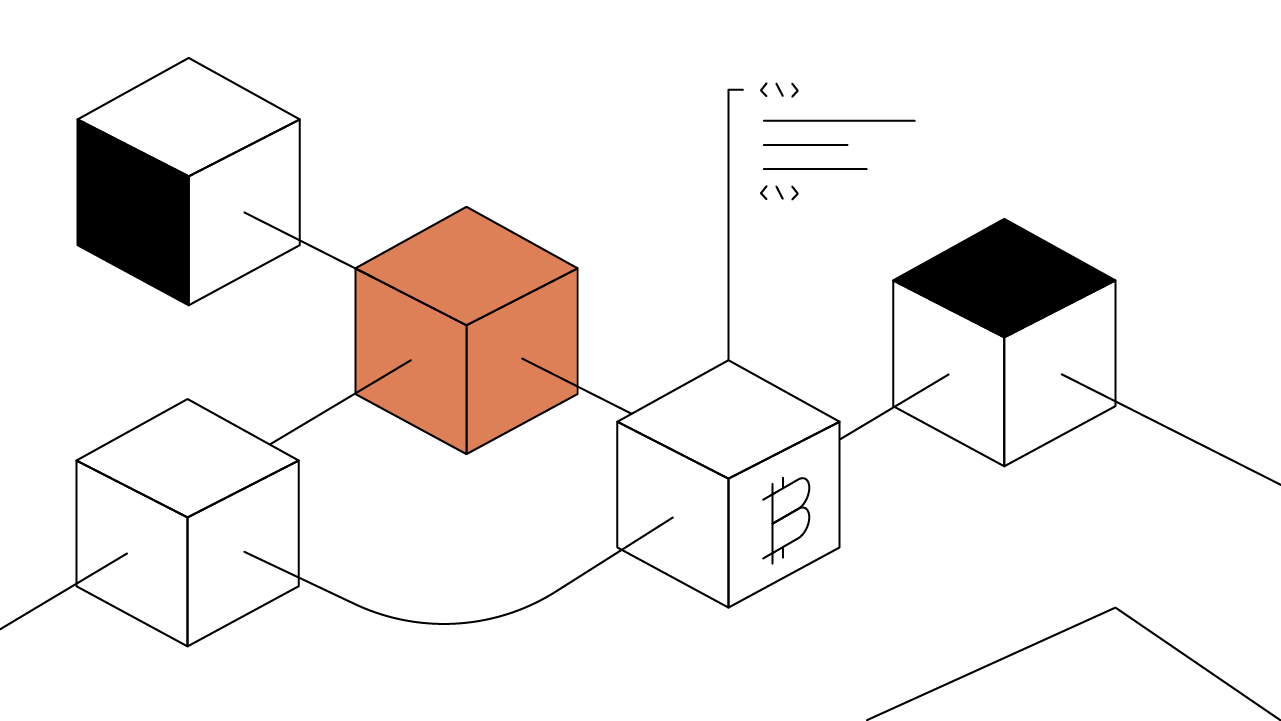
What Is Bridging?
Learn how crypto bridges work, and the role they play in the interconnected crypto ecosystem.
Updated October 7, 2024 • 2 min read
Summary
A crypto bridge enables the transfer of assets or data between different blockchain networks, expanding the interconnectivity and interoperability across different protocols. They typically function by locking assets on one blockchain and issuing an equivalent number of "wrapped" tokens on another, ensuring a value of 1:1 between them. Using bridges can also involve risks including security vulnerabilities, and concerns relating to centralization.
With more choice of blockchains to use than ever before, there has never been more demand to easily transfer assets between them. In the early days of cryptocurrency, there were very limited means of doing so. Today however, participants in the crypto ecosystem can use what is known as a “bridge” to do this. We’re taking a look at what they are and how they are used to increase the interoperability of different blockchain networks.
Many blockchains use their own means of executing, verifying and recording transactions, meaning that their token standards and processes are often incompatible with others. Bridges can solve this problem, by allowing the assets stored on one blockchain to be transferred onto another. These tools can either be “trust-based” (which means they rely on a central authority to verify the asset transfer) or “trustless” (meaning that smart contracts are used to ensure that the transaction has occurred as expected).
How Do They Work?
To achieve this transfer of assets, despite chains not having shared rules or processes, bridges often use a process called “wrapping.” This involves taking the asset the user wishes to transfer, and creating a “wrapped” version on the destination chain. For example, BTC being sent to the Ethereum blockchain would become “wrapped BTC” or “WBTC”, minted on the Ethereum blockchain.
To do this, the original asset becomes locked in a reserve on its origin chain, to ensure that it is not being duplicated and that it retains its full value on the destination chain. If it becomes necessary to transfer the asset back to its original chain (in this case the Bitcoin blockchain), then the wrapped version can be burned and the original asset can be unlocked and removed from the reserve.
What Are Some of the Risks?
While this bridging adds to the interconnectedness of the crypto ecosystem, it is not without risks. Lessened security is one of the most significant threats posed, as bridges can often represent a single, centralized point of failure for bad actors. Some of the highest profile crypto hacks have resulted from bridging protocols being exploited, including the $100 million hack of Horizon and the $190 million hack of Nomad, both of which occurred in 2022. The methods of attack for this kind of exploit vary, but usually involve exploiting vulnerabilities in the smart contracts of such protocols in order to drain locked funds.
The fact that certain bridging protocols rely on a central authority can also introduce its own risks. If the group involved in running the bridge were to act maliciously, the locked funds could potentially be stolen, with or without the asset owner’s knowledge.
Crypto bridges allow for greater interoperability between blockchain networks by allowing data and assets to be transferred conveniently. However, it’s important for both individuals and organizations to be aware of the risks that they carry when deciding to use them. As the crypto ecosystem continues to evolve, so too will the level of sophistication and security offered by bridges. For the time being however, enjoy the convenience they offer with caution!
Cryptopedia does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Cryptopedia article are solely those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions of Gemini or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice. A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions. Please visit our Cryptopedia Site Policy to learn more.

Is this article helpful?