Contents
What Is Blockchain? The Tech Behind Crypto Explained
Discover how blockchain technology works, its key features, and how it's revolutionizing finance, healthcare, supply chains, and digital security.
Updated March 11, 2025 • 5 min read
Summary
The world is moving toward a digital-first economy, and blockchain technology is central to this transformation. So, what is blockchain technology, and why has it been hailed as one of the most revolutionary innovations of the 21st century? While blockchain is widely known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its impact extends to finance, healthcare, supply chains, and even identity verification. If you have ever used Bitcoin, Ethereum, or another cryptocurrency, you have already interacted with blockchain technology. However, there’s much more to blockchain than digital currencies.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
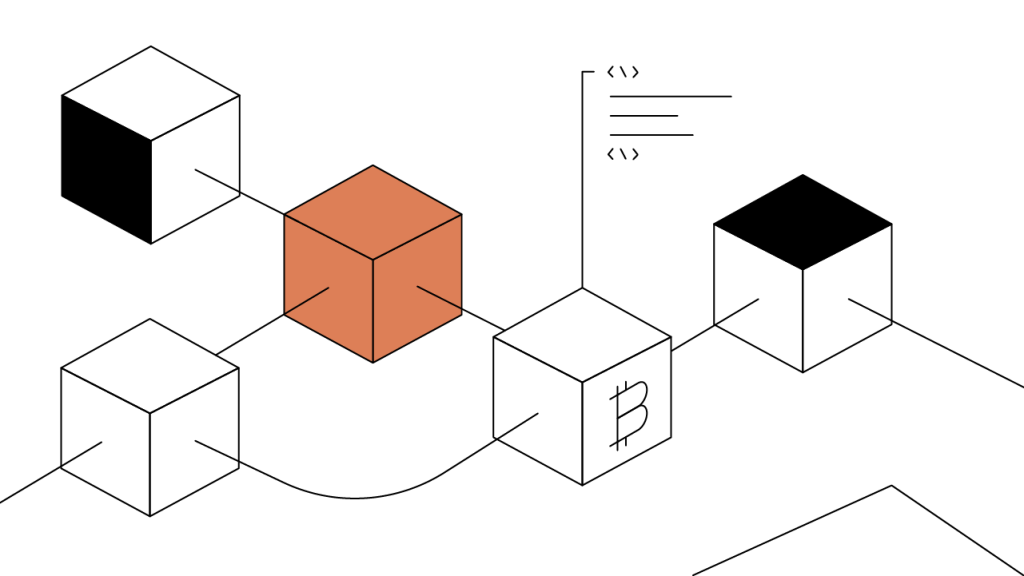
Think of blockchain as a digital ledger — a distributed ledger — that records transactions securely and transparently. Unlike traditional databases, where data is stored in one central location, blockchain networks distribute information across multiple nodes, ensuring data security and immutability.
With blockchain technology:
Data is grouped into blocks and connected in a chain-like structure.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable link.
Transactions are verified through consensus mechanisms instead of relying on a third party (like a bank).
Blockchain technology is designed to be resistant to tampering, transparent, and highly secure, making it ideal for industries where trust and security are critical.
What Are the Key Features of Blockchain?
Blockchain technology has a handful of key features that are useful to understand:
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating central control. Transactions are verified by multiple nodes, ensuring security, trust, and reliability.
Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered or deleted. Cryptographic linking ensures data integrity, making blockchain ideal for financial records and supply chains.
Security and Transparency: Blockchain’s encryption and distributed ledger prevent fraud and cyber attacks. Public blockchains offer real-time transparency and audibility.
Smart Contracts: These self-executing agreements remove intermediaries, cutting costs and errors. They are tamper-proof and secure in finance, real estate, and logistics.
Efficiency and Speed: Transactions process within minutes, eliminating bank delays and high fees. Blockchain enables fast, low-cost global transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To truly understand blockchain technology, it is important to break down how transactions are processed. Blockchain transactions follow a structured process to ensure security, transparency, and decentralization.
Transaction Initiation
A user initiates a transaction, such as sending cryptocurrency, executing a smart contract, or recording data.
Unlike traditional banking, blockchain transactions bypass central authorities and await network validation. Gemini's secure exchange platform enables users to engage in blockchain transactions seamlessly, offering a reliable gateway into the digital asset space.
Verification and Consensus
Once a transaction is created, it is sent to network nodes (validators) for verification. These nodes ensure the transaction follows the network’s rules — preventing fraudulent or duplicate transactions.
Two main consensus mechanisms validate transactions.
The first is Proof of Work (PoW), which is the original method. PoW is used in Bitcoin mining as well as for other cryptocurrencies. With this method, miners solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain ledger.
PoW requires significant computing power and energy consumption but ensures high security. It also consumes a large amount of energy, making it less sustainable for mass adoption.
On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) is an energy-efficient alternative used in newer blockchain models like Ethereum 2.0. Instead of competing in a race to solve puzzles, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. It requires significantly less energy compared to PoW, and validators can lose their staked coin if they attempt fraudulent transactions.
The consensus mechanism ensures that every transaction added to the blockchain is valid and secure, making blockchain networks trustless and decentralized.
Block Creation and Addition
The verified transactions are grouped into blocks through cryptographic linking to retain previous block information. The chain-like structure protects records and data integrity from being tempered.
Finalization and Security
Tamper-proof security is ensured by distributing block data to multiple nodes. The verification process of every transaction eliminates dependency on third-party trust networks, which decreases fraud and financial risks.
How Is Blockchain Transforming Industries?
Blockchain’s impact extends beyond cryptocurrency, offering security, efficiency, and transparency across multiple sectors. By eliminating intermediaries, reducing fraud, and increasing data security, businesses worldwide are integrating blockchain to improve operations.
Here’s how:
Finance: Secure Transactions and Lower Costs
Users can perform peer-to-peer transactions through blockchain without needing bank intermediaries, which allows them to spend lower fees and faster settlements while transactions. Such developments create financial inclusion and the unbanked population can access financial services.
Real-World Use: Financial institutions apply blockchain Technologies to achieve real-time cross-border payments which stop fraud while providing digital transaction automation.
Healthcare: Protecting Patient Data and Privacy
Through blockchain, patients receive secure, immutable storage records which can enhance data privacy with protection against medical fraud. By using blockchain, patients and healthcare providers maintain safe communication channels to exchange patient history content while securing critical health data.
Real-World Use: Medical establishments and Pharmaceutical entities operate blockchain systems that track drug product authenticity throughout their supply chain journey.
Supply Chain: Transparency and Product Tracking
New applications of blockchain Let companies track product movements through real-time logging, which decreases instances of fraud and counterfeiting while reducing operational inefficiency. The practice enables better visibility in worldwide supply chain operations.
Real-World Use: The retail company Walmart uses blockchain technology to monitor food deliveries, which decreases product loss while enhancing product recall capability.
Smart Contracts: Automating Legal and Business Agreements
When smart contracts fulfill their requirements, they activate agreements without requiring traditional business intermediaries such as lawyers and brokers. This process decreases expenses and removes human mistakes that lead to improved transaction efficiency.
Real-World Use: Businesses agreements and property sales operated by real estate companies and legal firms, work with smart contracts to establish tamper-proof digital transactions.
Cross-Border Payments: Faster and More Affordable Transactions
Traditional international payment processes need several days to complete operations and generate substantial fees. Blockchains allow quick worldwide transaction processing, which makes them useful for inexpensive remittance operations.
Real-World Use: Digital payment systems managed by Ripple and central banks investigate blockchain technology to execute secure funds transfers using a method without third-party involvement.
What Are Some Limitations of Blockchain?
While blockchain offers innovation, it faces several challenges:
Scalability Issues: Networks like Ethereum struggle with slow speed and high transaction fees.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The government imposes varying regulations, affecting Global adoption.
Energy Consumption: The PoW mechanism requires significant computing power, impacting sustainability.
Adoption Barriers: Businesses need time and resources to integrate blockchain into operations.
Developers are advancing next-gen blockchain solutions to overcome these challenges.
What To Know About the Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain continues to evolve, paving the way for ground-breaking innovations. Here’s what's next:
Web3 Development
The third version of the internet, known as Web3, operates through blockchain fundamentals to abolish single-pointed control systems. Web3 allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps), which provide users full ownership of their data and complete privacy while conducting online transactions.
Web3 shifts influence away from corporations to give individuals complete power so it transforms financial systems in addition to social media and digital content ownership practices.
Integration With AI and IoT
Blockchain unites with artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) systems to establish safer, automated, and transparent network systems.
Blockchain efficiency grows because AI optimizes data processing and security functions with IoT devices that store and verify information through centralized blockchain networks. The merged technology improves operations in smart cities and autonomous vehicles with healthcare institutions.
Mass Adoption
Various entities including businesses, banks, and governments, actively adopt blockchain-based structures to deliver safe deals and validate identities while supervising supply chains.
The advancement of regulation and scalability will drive blockchain adoption into financial sectors and real estate markets, as well as the logistics and public service sectors. The growth of the blockchain infrastructure system will produce a digital platform that delivers both efficiency in reducing costs and enhancing system transparency.
As blockchain technology advances, it will continue reshaping industries and redefining how digital transactions operate in the modern world.
The Bottom Line
The introduction of blockchain technology enables new modern methods of digital transactions, automation, and securities of digital communications.
Businesses experience industrial transformation through blockchain’s decentralized tamper-proof nature, especially through borderless payments, self-executing smart contracts, and transparent supply chains. Various organizations have now implemented blockchain technology into their businesses, which leads us toward a secure and efficient future with improved trust levels.
Join Gemini and get started with crypto.
Cryptopedia does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Cryptopedia article are solely those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions of Gemini or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice. A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions. Please visit our Cryptopedia Site Policy to learn more.

Is this article helpful?